Ouch, that is a strong statement. It likely needs softened, but, there is some truth within those words.
Last night we did our monthly lecture on www.onlineCE.com. We had a packed room, biggest audience to date. It is likely because people are realizing that the small stuff matters. We talked for an hour on foot types and how they present, how they potentially load, and how other mechanical issues above can impact how a foot type loads.
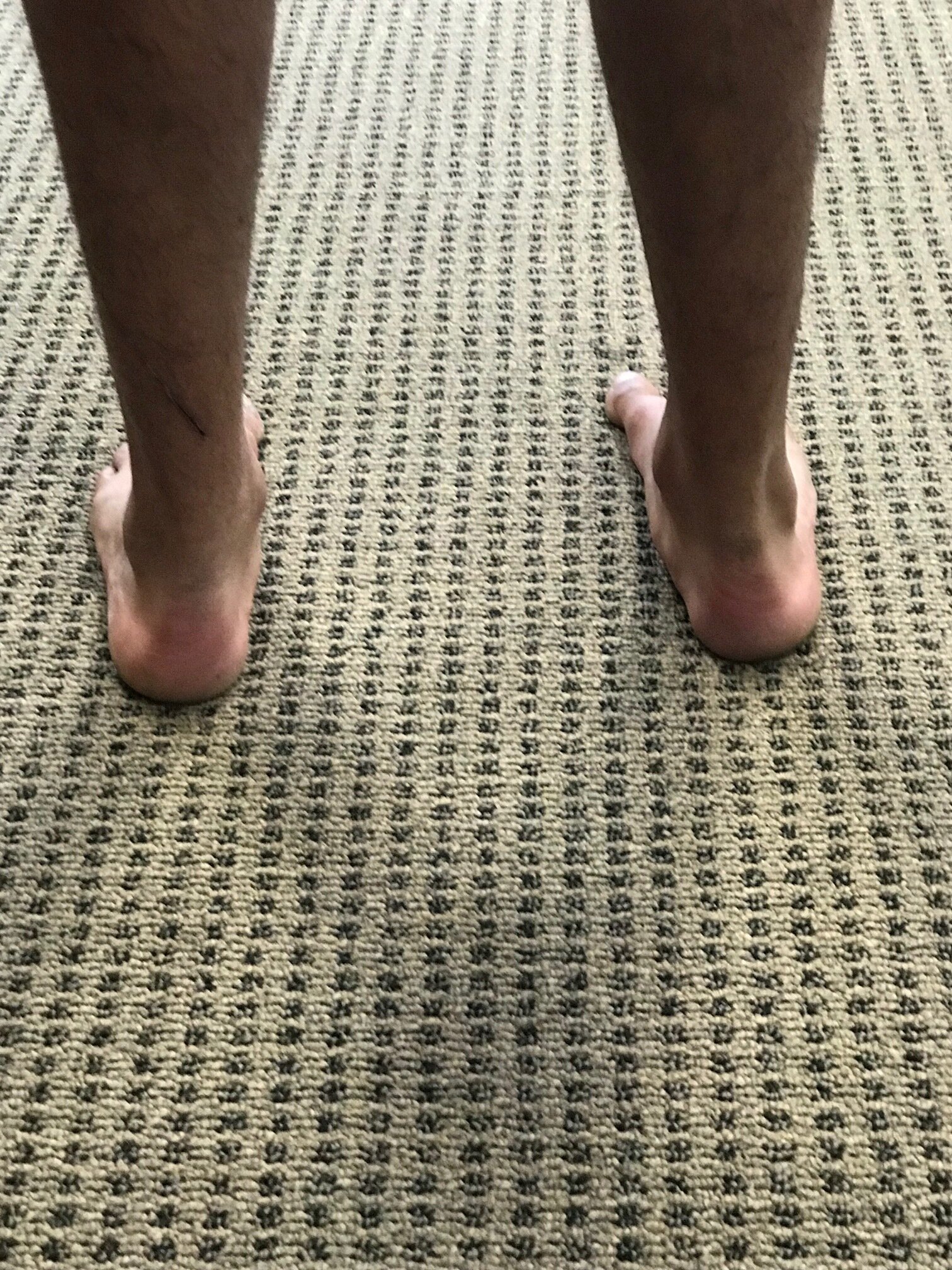
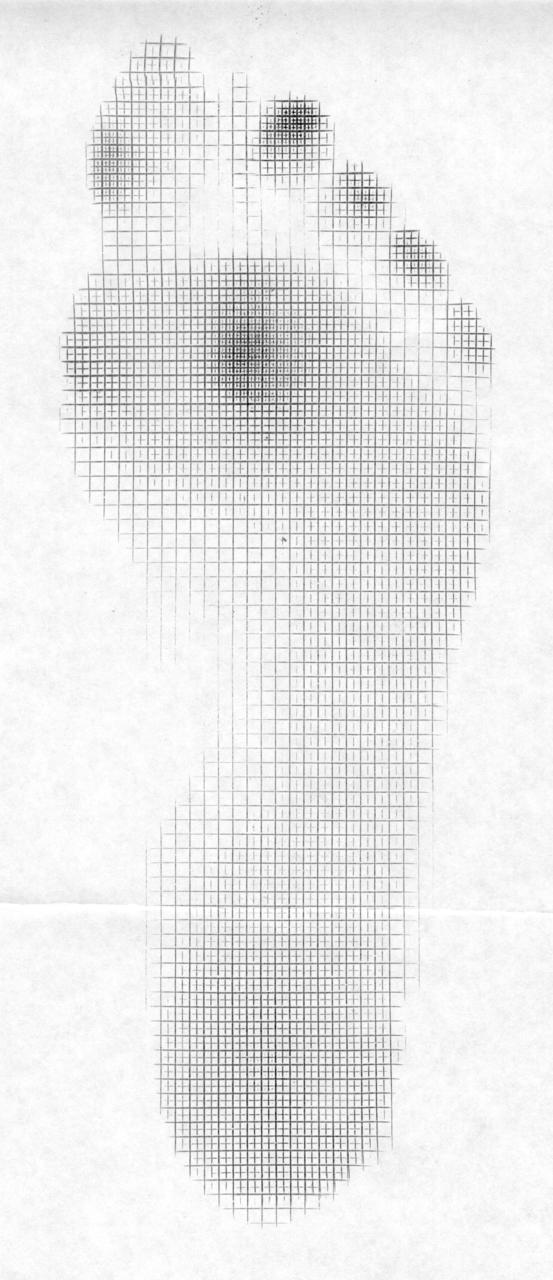
We have all seen the pedographs like in the photo. The unwise depend on a static pedograph mapping for diagnostic help and God forbid that is all you use for making orthotics (that may only help if your client is a professional stander), the more wise use the dynamic pedograph mapping to see how their client moves across the ground, and the wise use it as a mere piece of the data, combine it with a clinical exam, look far up into the biomechanical chain for other locomotive challenges that could change the dynamic loading pattern across the foot and ground. What do we mean exactly ? Well, a client with a rearfoot valgus foot type will load the heel and rest of the foot one way if they are doing a good job stacking the hip over the knee, and knee over the foot. But, if they have weakness in the hip affording a frontal plane drift of the pelvis over the foot, that is going to magnify the rearfoot valgus loading pattern (addendum: they could also tip into rearfoot varus posturing as well). That is just one example, of many. In otherwords, it is the same foot type, but both of these are going to show a dynamic change in the loading pattern response. So, said another way, you cannot diagnose a foot type by the pedograph mapping. Nor should one make an orthotic for someone based off of a pedograph mapping, nor without an examination of the entire kinetic change. What is your client able, and unable, to do? That is a big question, and when you start by asking those 2 questions, you get closer to the prize. The pedograph only shows the static or dynamic pressures from the superincumbent load, it does not tell you if it is good or bad, and it does not tell you what they are doing, or why they are loading that way. It only shows the loading. Your job is to find out why they are loading that way, and then determine if that is part of their problem they have sought you out for.
So, does your head spin now ? Does this suddenly make you sweat ? Do you realize you are missing pieces of the pie in helping your client? Not yet maybe ? How about this then, you have someone with a rearfoot valgus with internal tibial torsion. How are they going to load now? What if you throw in a valgus knee and femoral torsion variant? Are they going to pronate more or less ? What if that person had just internal tibial torsion on one leg and not the other, yet they had two rearfoot valgus feet presentations. Now what? Suddenly the loading is different in both feet and up the chains. There is likely going to be different challenges to limb spin control from side to side. This aberrant and asymmetrical loading is going to come up to a pelvis, upon which a single spinal column is trying to find a sound base of support and mobility to work and transfer loads from.
And, what if this client also has some tibial varum on that same side ? What if they had external tibial torsion or some femoral torsional presentation on one side ? You can see now how complicated this gets. And that is just on the structural components. What about the dynamic components ? We here at The Gait Guys feel that this is all critical stuff to take into consideration and it is sometimes the stuff that is the tipping point between a successful management of a clients complaints, and unsuccessful.
In closing, think about this. If you are sending out your orthotics for fabrication, have you conveyed this all to your fabricator ? All they know is what a pedograph might show, and what the foot mold looks like. You have to provide them with all this other information, because essentially they are blind (this of course assumes your fabricator can mind juggle all the torsions, valgus/varus, pelvis drift loads etc, oy vey ! That is hard to do !) This is why we do all of our modifications in office, in the rare case we need a temporary orthotic modification. But, we will aim to just correct what mechanics are aberrant and avoid the whole orthotic crutch when we are able. But lets face it, sometimes, for a period of time, we all need a crutch to get through a problem, to find better mechanics where we can strengthen from or gain protecting from temporarily. That is what splints do, taping, crutches, braces, one might even argue what corrective exercises do. It is a path on the journey for your client, and sometimes they need help through the muddy parts.
And, don't be "that guy" that says orthotics are useless. They are a crutch , a tool. A small tool, one might argue that it should only be pulled out when the other tools are not working to get the job done. Do not make them your first line of defense, except when that is called for. After all, not all people were blessed with sufficient anatomical and mechanical parts to avoid needing a crutch, so don't be "that guy" that preaches from that extreme, because it is not honest. Or, maybe, you just do not see the biomechanical messes we see in our clinics, that is quite the realistic possibility.
Want to learn more about this kind of stuff? Keep up with our blog here. OR take some of our lecture recorded classes on www.onlineCE.com . We have a library of classes there for you to take anytime. And meet us once a month over there, every 3rd Wednesday. And, stay tuned for some new teaching gigs we have coming your way.
-Shawn and Ivo, the gait guys