Gaining Anterior Length, Through Posterior Strength and vice versa….A Lesson in Reciprocal Inhibition
I found a really cool article, quite by accident. I was leafing through an older copy of one of, if not my favorite Journals “Lower Extremity Review” and there it was. An article entitled “Athletes with hip flexor tightness have reduced gluteus maximus activation”. Wow, I thought! Now there is a great article on reciprocal inhibition! This reminded me of a piece we wrote some time ago
What is reciprocal inhibition, also called “reciprocal innervation” you ask? The concept, was 1st observed as early as 1626 by Rene Descartes though observed in the 19th century, was not fully understood and accepted until it earned a Nobel prize for its creditor, Sir Charles Sherrington, in 1932.
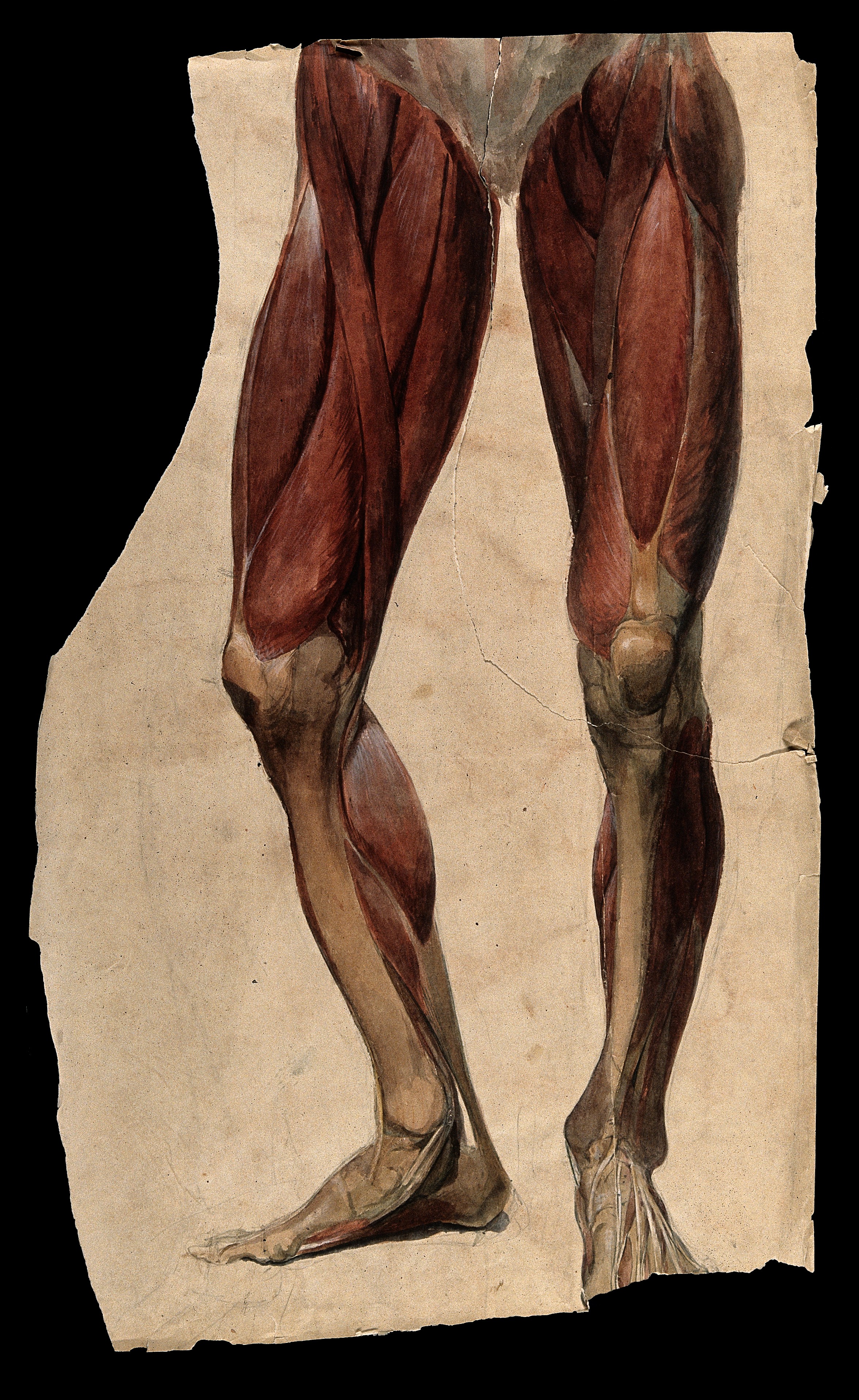
Simply put, when a muscle contracts, its antagonist is neurologically inhibited (see the diagram above) When your hip flexors contract, your hip extensors are inhibited. This holds true whether you actively contract the muscle or if the muscle is irritated in some manner, causing contraction. The reflex has to do with muscle spindles and Type I and Type II afferents which I have covered in an article I wrote some time ago.
We can (and often do) take advantage of this concept with treating the bellies of hip flexors (iliopsoas, tensor fascia lata, rectus femoris, iliacus, iliocapsularis) and extensors (gluteus maximus, posterior fibers of gluteus medius). This is especially important in folks with low back pain, as they often have increased psoas activity and cross sectional area, especially in the presence of degenerative changes.
There also appears to be a correlation between decreased hip extension and low back pain, with a difference of as little as 10 degrees being significant. Take the time to do a thorough history and exam and pay attention to hip extension and ankle dorsiflexion as they should be the same, with at least 10 degrees seeming to be the “clinical” minimum. Since the psoas should only fire at the end of terminal stance/preswing and into early swing, problems begin to arise when it fires for longer periods.
Can you see now how taking advantage of reciprocal inhibition can improve your outcomes? Even something as simple as taping the gluteus can have a positive effect! Try this today or this week in the clinic, not only with your patients hip flexors, but with all muscle groups, always thinking about agonist/antagonist relationships.
In the moment: Sports medicine Jordana Bieze Foster: Athletes with hip flexor tightness have reduced gluteus maximus activation Lower Extremity review Vol 6, Number 7 2014
https://tmblr.co/ZrRYjx1VG3KYy
Mills M, Frank B, Blackburn T, et al. Effect of limited hip flexor length on gluteal activation during an overhead squat in female soccer players. J Athl Train 2014;49(3 Suppl):S-83.
Ciuffreda KJ, Stark L. Descartes’ law of reciprocal innervation. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1975 Oct;52(10):663-73.
Jacobson M Foundations of Neuroscience Springer Science and Business Media, Plenum Press, NY 1993 p 277
http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1932/sherrington-bio.html
https://thegaitguys.tumblr.com/post/9708399904/ah-yes-the-ia-and-type-ii-afferents-one-of-our
Arbanas J, Pavlovic I, Marijancic V, et al MRI features of the psoas major muscle in patients with low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2013 Sep;22(9):1965-71. doi: 10.1007/s00586-013-2749-x. Epub 2013 Mar 31.
Roach SM, San Juan JG, Suprak DN, Lyda M, Bies AJ, Boydston CR. Passive hip range of motion is reduced in active subjects with chronic low back pain compared to controls. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015 Feb;10(1):13-20. Erratum in: Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015 Aug;10(4):572.
Paatelma M Karvonen E Heiskanen J Clinical perspective: how do clinical test results differentiate chronic and subacute low back pain patients from “non‐patients”? J Man Manip Ther. 2009;17(1):11‐19.[PMC free article] [PubMed]
Evans K Refshauge KM Adams R Aliprandi L Predictors of low back pain in young adult golfers: a preliminary study. Phys Ther Sports. 2005;6:122‐130.
Mellin G Correlations of hip mobility with degree of back pain and lumbar spinal mobility in chronic low‐back pain patients. Spine. June 1988;13(6):668‐670. [PubMed]
Lewis CL, Ferris DP. Walking with Increased Ankle Pushoff Decreases Hip Muscle Moments. Journal of biomechanics. 2008;41(10):2082-2089. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.05.013.
Nodehi-Moghadam A, Taghipour M, Goghatin Alibazi R, Baharlouei H. The comparison of spinal curves and hip and ankle range of motions between old and young persons. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran. 2014;28:74.
Daniel Moon , MD, MS; Alberto Esquenazi , MD Instrumented Gait Analysis: A Tool in the Treatment of Spastic Gait Dysfunction JBJS Reviews, 2016 Jun; 4 (6): e1. http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.15.00076
Kilbreath SL, Perkins S, Crosbie J, McConnell J. Gluteal taping improves hip extension during stance phase of walking following stroke. Aust J Physiother. 2006;52(1):53-6.