Toes Spacers, anyone?
/Less pain through better mechanics?
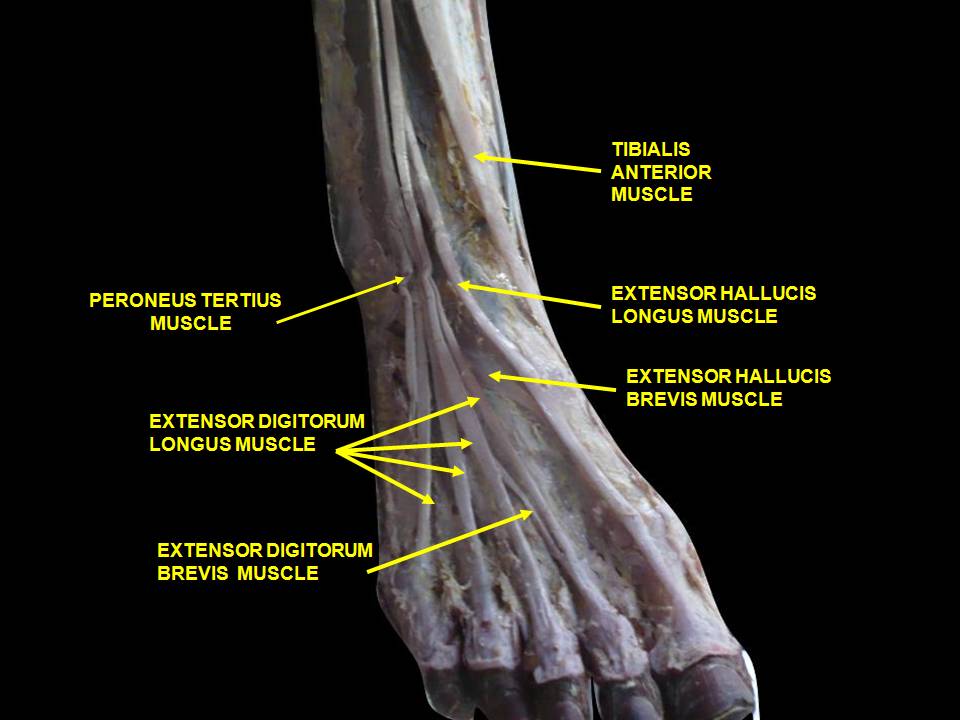
We have been using toe separators for various foot problems like hallux valgus, hammer toes and flexor dominance/extensor weakness. Our reasoning is that through changing the angle of attachment of the muscle, you alter the mechanical advantage of that muscle and help it to work more efficiently. This seems implied in the literature with respect to foot orthoses (1-3) but we could not find any data regarding toe separators. Toe separators DO seem to reduce pain and increase function (4-6). Perhaps this is through better biomechanics, mechanical deformation, proprioceptive changes, or most likely a combination of all these factors and more. We think clinical results speak volumes. It is nice to see more data coming out on these easy to implement clinical tools.
What is you clinical reasoning or rationale for using these devices? We would love to hear and if you have an article for reference you could share, that would be great.
1. Scherer PR, Sanders J, Eldredge DE, Duffy SJ, Lee RY. Effect of functional foot orthoses on first metatarsophalangeal joint dorsiflexion in stance and gait. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006 Nov-Dec;96(6):474-81.
2. Halstead J, Chapman GJ, Gray JC, Grainger AJ, Brown S, Wilkins RA, Roddy E, Helliwell PS, Keenan AM, Redmond ACFoot orthoses in the treatment of symptomatic midfoot osteoarthritis using clinical and biomechanical outcomes: a randomised feasibility study. Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;35(4):987-96. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2946-6. Epub 2015 Apr 28.
3. Bishop C, Arnold JB, May T. Effects of Taping and Orthoses on Foot Biomechanics in Adults with Flat-Arched Feet. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016 Apr;48(4):689-96. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000807.
4. Chadchavalpanichaya N, Prakotmongkol V, Polhan N, Rayothee P, Seng-Iad S. Effectiveness of the custom-mold room temperature vulcanizing silicone toe separator on hallux valgus: A prospective, randomized single-blinded controlled trial. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2017 Mar 1:309364617698518. doi: 10.1177/0309364617698518. [Epub ahead of print]
5. Tehraninasr A, Saeedi H, Forogh B, Bahramizadeh M, Keyhani MR. Effects of insole with toe-separator and night splint on patients with painful hallux valgus: a comparative study. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2008 Mar;32(1):79-83. doi: 10.1080/03093640701669074.
6. Tang SF, Chen CP, Pan JL, Chen JL, Leong CP, Chu NK. The effects of a new foot-toe orthosis in treating painful hallux valgus. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002 Dec;83(12):1792-5.