What did you notice? The Devil is in the details...
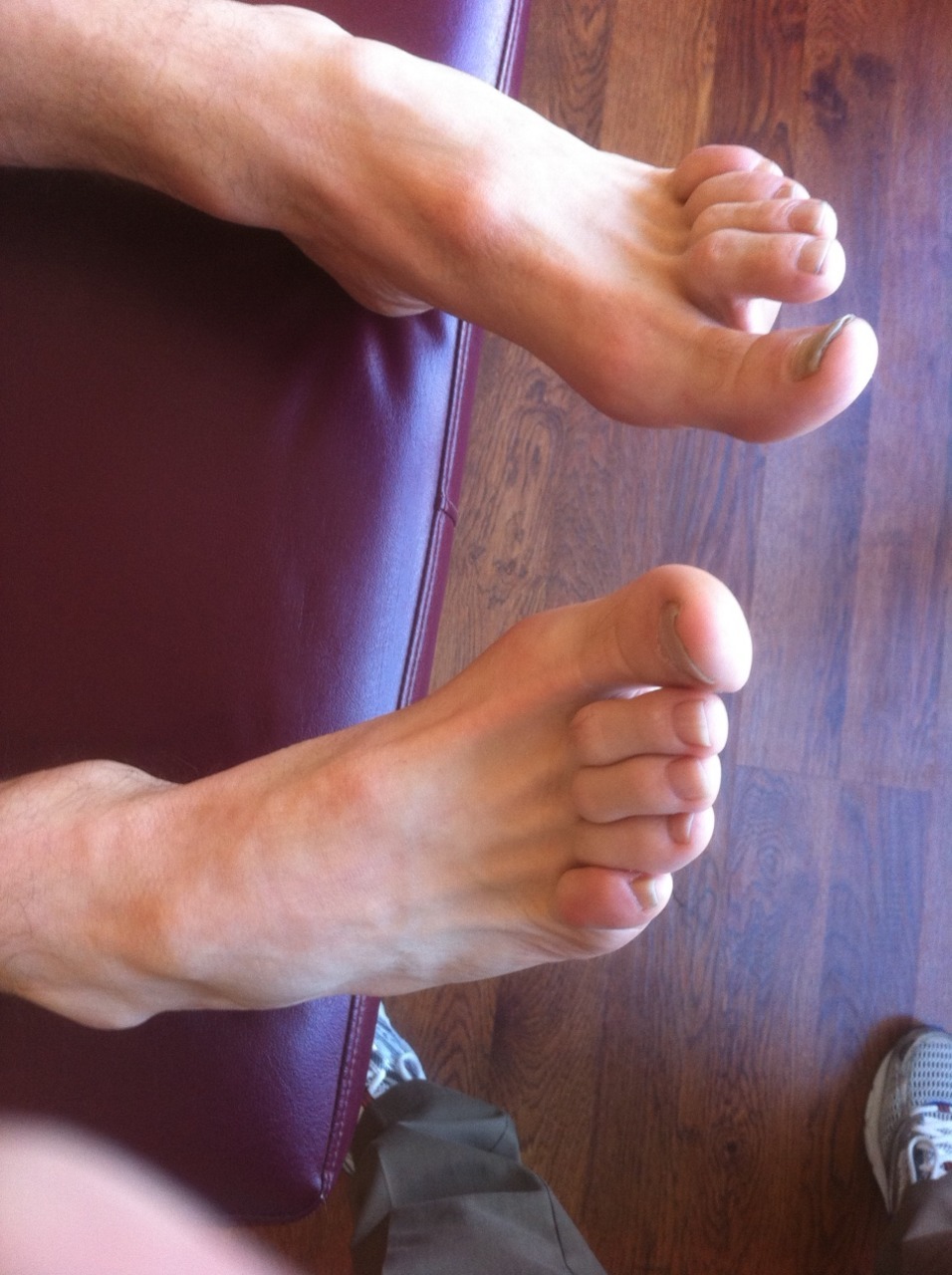
/Cavus foot? Loss of the transverse arch? Prominence of extensor tendons?
The question is: Why?
It’s about reciprocal inhibition. The concept, though observed in the 19th century, was not fully understood and accepted until it earned a Nobel prize for its creditor, Sir Charles Sherrington, in 1932. Simply put, when a muscle contracts, its antagonist is neurologically inhibited, So when your bicep contracts, your tricep is inhibited. This holds true whether you actively contract the muscle or if the muscle is irritated (causing contraction).
So how does this apply to this foot?
We see prominence of the extensor tendons (particularly the extensor digitorum brevis EDB; the longus would have caused extension at the distal interphalangeal joint). The belly of the muscle is visible, telling us that it is active. It is neurologically linked to the flexor digitorum brevis (FDB). This muscle, in turn, has slips which attach it to the abductor hallucis brevis (AHB) medially and the abductor digiti minimi (ADM) laterally. These muscles together form 2 triangles (to be discussed in another post) on the bottom of the foot, which lend to the stability of the foot and the arches, especially the transverse.
When the EDB fires, it inhibits the FDB, (which, in addition to flexing the MTP’s, assists in maintaining the arch). The EDB has an effect which drops the distal heads of the metatarsals as well (Hmm, think about all the people with met head pain) Now, look at the course of the tendons of the EDB. In a cavus foot, there is also a mild abductory moment, which flattens the arch. Conversely, the FDB in a cavus foot would serve to actually increase the arch, and would have a ,mild adductory moment. Net result? A flattened transverse arch.
Now look at the Flexor digitorum longus, overactive in tbis foot (as evidenced by the flexion of the distal interphalangeal joints, mild adduction of the toes (due to the change of direction of pull in a cavus foot) and lowering of the met heads due to hyperextesnion at the MTP joints ). This mm is reciprocally linked with the extensor digitorum longus. The prominence of the extensor tendons is do to increased activity of the EDB (go ahead, extend all your fingers and look at the tendons in your hand. Now flex the DIP and IP joints and extend the MTP; see how they become more prominent?).
Reciprocal inhibition. It’s not just for dinner anymore…
We are and remain; The Gait Guys