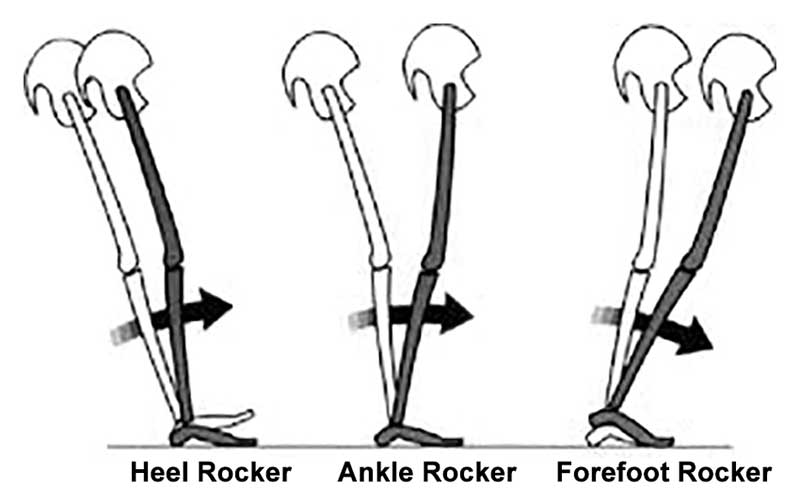
Do you know where your rocker is?
At 1st pass, some articles may seem like a sleeper, but there can be some great clinical pearls to be had. I recently ran across one of these. It was a presentation from the 42nd annual American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists meeting in Orlando, March 2016 entitled “ Shifting Position of Shoe Heel Rocker Affects Ankle Mechanics During Gait”. The title caught my eye.
They looked at ankle kinematics while keeping the toe portion of rocker constant at 63% of foot length, angled at 25 degrees and shifting the base of a rockered shoe from 1cm behind the medial malleolus, directly under it and 1cm anterior to it. Knee and hip kinematics did not differ significantly, however ankle range of motion did.
The more forward the ankle rocker, the less plantarflexion but more ankle dorsiflexion at midstance. So, the question begs, why do we care? Lets explore that further…
- Think about the “average” heel rocker in a shoe. It largely has to do with the length of the heel and heel flare (base) of the shoe. The further back this is (ie; the more “flare”) the more plantar flexion at heel strike and less ankle dorsiflexion (and thus ankle rocker, as described HERE) you will see. Since loss of ankle dorsiflexion (ie: rocker) usually means a loss of hip extension (since these 2 things should be relatively equal during gait (see here), and that combination can be responsible for a whole host of problems that we talk about here on the blog all the time. Picking a shoe with a heel rocker based further forward (having less of a flare) would stand to promote more ankle dorsiflexion.
- Having a shoe with a greater amount of “drop” from heel to toe (ie: ramp delta) is going to have the same effect. It will move the calcaneus forward with respect to the heel of the shoe and effectively move the rocker posteriorly.
- Lastly, look a the shape of the outsole of the shoe. The toe drop is usually clear to see, but does it have a heel rocker (see the picture above)?
These are a few examples of what to look for in a clients shoe when examining theirs or making a recommendation, depending on whether you are trying to improve or decrease ankle rocker. We can’t think of why you would want to decrease ankle rocker, but with conditions like rigid hallux limitus, where the person has limited or no dorsiflexion of the great toe, you may want to employ a rockered sole shoe. We would recommend one with the rocker set more forward.