Knee pain and the the semitendinosis?
/image source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Slide2DADE.JPG
The semitendinosus hails from the posterior compartment.
During an ideal gait cycle, the semitendinosus from mid swing through nearly loading response, with a brief firing at toe off.
We remember that the abdominals should initiate thigh flexion with the iliopsoas, rectus femoris, tensor fascia lata and sartorius perpetuating the motion. Sometimes, when the abdominals are insufficient, we will substitute other thigh flexors, often the psoas and/or rectus femoris, but sometimes sartorius, especially in people with excessive midfoot pronation. Think about all of the medial rotation occurring at the knee during excessive midfoot pronation and when overpronation occurs, the extra compensatory external rotation that must occur to try and bring the knee back into the sagittal plane. The sartorius is positioned perfectly for this function, along with the semitendinosus which assists and external rotation and closed chain.
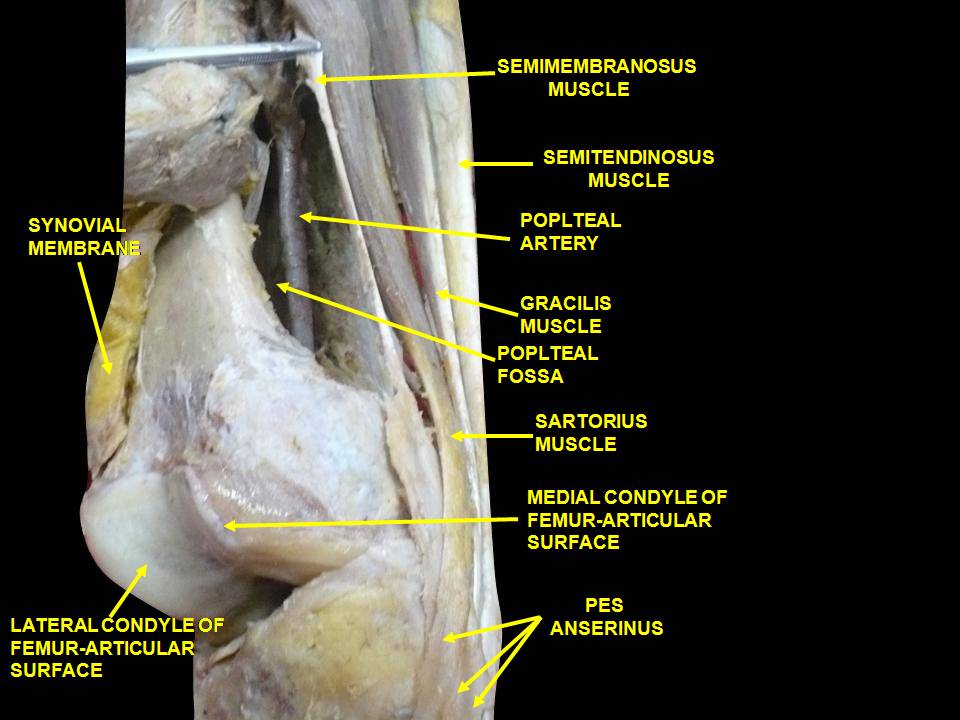
The semitendinosis is the most superficial of the hamstrings and originates between the biceps femoris, with which it shares a common tendinous attchment, which is anterior and slightly lateral and the semimembranosis which is just beneath it and slightly medial. It is fusiform and the muscle body ends about mid thigh, before becoming a long "piano string" and ultimately inserting most inferiorly of the trio, below the gracilis, on the pes anserine.
Call it pes anserinus bursitis or pes anserine tendinitis but they both add up to medial knee pain when the thigh needs help flexing. Look to this troublesome trio the next time you have recalcitrant medial knee pain.
Dr Ivo Waerlop, one of The Gait Guys
#gait, #gaitanalysis, #gaitdysfunction, #thegaitguys, #pesanserine, #semitendinosis
Imani F, Rahimzadeh P, Abolhasan Gharehdag F, Faiz SH. Sonoanatomic variation of pes anserine bursa. Korean J Pain. 2013;26(3):249-54.
Gupta, Aman & Saraf, Abhinesh & Yadav, Chandrajeet. (2013). ISSN 2347-954X (Print) High-Resolution Ultrasonography in PesAnserinus Bursitis: Case Report and Literature Review. 1. 753-757.
Gray H: Anatomy of the Human Body Lea and Febiger, Phildelphia and New York 1918
https://www.anatomy-physiotherapy.com/knee/articles/systems/musculoskeletal/lower-extremity/knee/test-your-knowledge-the-pes-anserinus
Michaud T: in Foot Orthoses and Other Forms of Conservative Foot Care Williams & Wilkins, 1993 Pp. 50-55
Michaud T: in Human Locomotion: The Conservative Management of Gait-Related Disorders 2011