Stretching part 2
/So, how can we utilize this reflex?
How about to activate a weak or lengthened muscle?
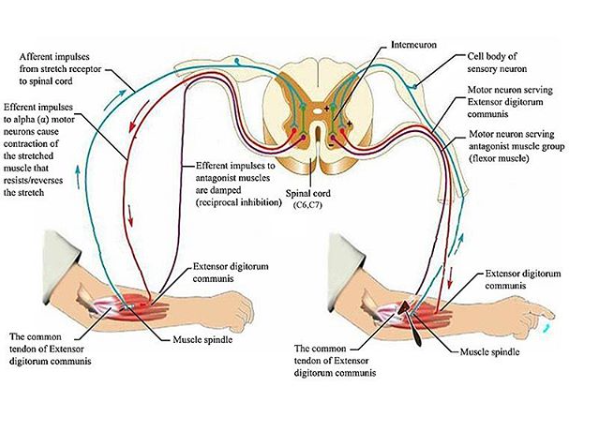
Did you notice the other neuron in the picture? There is an axon collateral coming off the Ia afferent that goes to an inhibitory interneuron, which, in turn, inhibits the antagonist of what you just stretched or activated. So if you acitvate one muscle, you inhibit its antagonist, provided there are not too many other things acting on that inhibitory interneuron that may be inhibiting its activity. Yes, you can inhibit something that inhibits, which means you would essentially be exciting it. This is probably one of the many mechanisms that explain spasticity/hypertonicity
How can we use this? How about to inhibit a hypertonic muscle?
Lets take a common example: You have hypertonic hip flexors. You are reciprocally inhibiting your glute max. You stretch the hypertonic hip flexors, they become more hypertonic (but it feels so good, doesn’t it?) and subsequently inhibit the glute max more. Hmm. Not the clinical result you were hoping for?
How about this: you apply slow stretch to the glutes (ie “reverse stretch”) and apply pressure to the perimeter, both of which activate the spindle and make the glutes contract more. This causes the reciprocal inhibition of the hip flexors. Cool, eh? Now lightly contract the glutes while you are applying a slow stretch to them; even MORE slow stretch; even MORE activation. Double cool, eh?
Don’t believe me, try this on yourself, your clients, patients, willing family members and pets.
Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_extensor_digitorum_reflex.jpg